


DIANA experiment to observe neural signal propagation in the thalamocortical pathway.
Verification of DIANA signal results through electrophysiological experiment.
in vitro experiments with Jurkat T-cell was performed to compare the increasing T2 at the two conditions.
T2 is plotted at conditions of membrane potential changes and cell swelling, controlled the concentraion of potassium and sodium ion.
Despite of measuring same pool si-ze ratio(PSR) in the conditions, T2 increasing was observed more rapidly at membrane potential change condition.

a) Extraction of respiratory and cardiac signals from navigating echoes by lowpass and bandpass filtering, respectively. Navigating echoes were obtained from the reception coils close to the diaphragm and pulmonary trunk, respectively, for perfusion and VW maps.
b) The QW map was generated by voxel-specific differences in the maximum and minimum values of all cardiac phase-resolved images after image registration.
c) The VW map was generated by voxel-specific differences in the end-expiration and end-inspiration images after image registration.

Structural, QW and VW images at coronal plane: CT/SPECT vs. UTE-MRI.
a) Structural CT image of a healthy 26-year-old female (left), SPECT QW image (middle), and SPECT VW image (right)
b) Structural UTE image (left), UTE-MRI QW map (middle), and UTE-MRI VW map (right).

UTE images and VW/QW maps based on them.
(a) Structural coronal UTE images of a 26-year-old healthy female (top) and a 24-year-old healthy male (bottom).
(b) UTE-MRI QW maps and (c) VW maps showing similar patterns for each subject: In regions close to the pulmonary arteries and veins in the QW map and higher signal intensities in the lower lobe of the VW map.

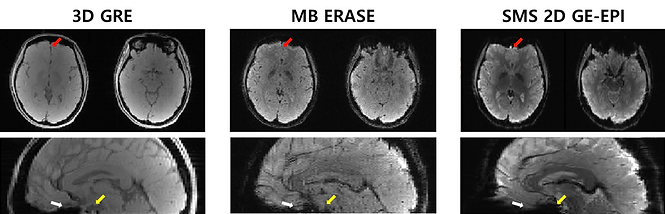
ERASE(Equal-TE Rapid Acquisition with Sequential Excitation) is a spatiotemporal encoding pulse sequence using a linearly frequency-swept chirp pulse.
We firstly implemented MB SPEN imaging using GRAPPA-type reconstruction.
ERASE sequence has a robustness to B0 homogeneities compared to EPI.
Accordingly, image distortion and signal loss are reduced and can be used as an alternative of EPI.
